SMALL
1. 정수 타입 (Integer Type)
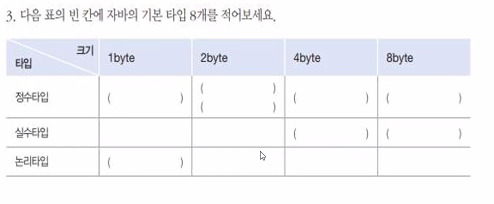
정수 타입은 소수점이 없는 정수값을 저장합니다. 자바에서 제공하는 정수 타입은 아래와 같습니다.
| byte | 8 | -128 ~ 127 | 0 |
| short | 16 | -32,768 ~ 32,767 | 0 |
| int | 32 | -2^31 ~ 2^31-1 | 0 |
| long | 64 | -2^63 ~ 2^63-1 | 0L |
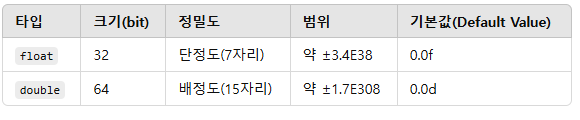
2. 실수 타입 (Floating-Point Type)
3. 논리 타입 (Boolean Type)
논리 타입은 참(true) 또는 **거짓(false)**의 두 가지 값만 저장할 수 있습니다.
타입크기(bit)값기본값(Default Value)
| boolean | 1 (사실상 JVM 구현에 따라 다름) | true, false | false |
5번 3
6번 4

- 8번: ④
- 9번: ①
- 10번: ②

오류 원인:
- v2와 v3는 각각 if 블록 내부에서 선언된 지역 변수입니다.
- 따라서, 블록을 벗어난 13, 14, 16번 라인에서 접근할 수 없어 컴파일 오류가 발생합니다.
정답:
- 오류가 발생하는 라인: 13, 14, 16
12번 문제: 프로그래밍 구현실습
- 임의의 시간을 초 단위로 입력받아 시간, 분, 초로 변환하기
- 입력된 초를 각각 시간, 분, 초로 나누어 출력해야 합니다.
- 예: 23456789초 → 6521시간 53분 9초
import java.util.Scanner; public class TimeConverter { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("초를 입력하세요: "); int totalSeconds = scanner.nextInt(); int hours = totalSeconds / 3600; // 시간 계산 int minutes = (totalSeconds % 3600) / 60; // 남은 초에서 분 계산 int seconds = totalSeconds % 60; // 남은 초 System.out.println(hours + "시간 " + minutes + "분 " + seconds + "초"); scanner.close(); } }
- 사각형의 대각선 좌표로 정사각형 확인 및 출력
- 두 좌표로 사각형을 정의하고, 정사각형인지 판별합니다.
- 조건:
- |x1 - x2| == |y1 - y2|이면 정사각형입니다.
-
import java.util.Scanner; public class SquareChecker { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("첫 번째 좌표 (x1, y1): "); int x1 = scanner.nextInt(); int y1 = scanner.nextInt(); System.out.print("두 번째 좌표 (x2, y2): "); int x2 = scanner.nextInt(); int y2 = scanner.nextInt(); if (Math.abs(x1 - x2) == Math.abs(y1 - y2)) { System.out.println("정사각형입니다."); } else { System.out.println("정사각형이 아닙니다."); } scanner.close(); } }
- 삼각형 확인
- 세 변의 길이를 입력받고 삼각형을 그릴 수 있는지 확인합니다.
- 조건: a + b > c, a + c > b, b + c > a
-
import java.util.Scanner; public class TriangleChecker { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("세 변의 길이를 입력하세요: "); int a = scanner.nextInt(); int b = scanner.nextInt(); int c = scanner.nextInt(); if (a + b > c && a + c > b && b + c > a) { System.out.println("삼각형을 만들 수 있습니다."); } else { System.out.println("삼각형을 만들 수 없습니다."); } scanner.close(); } }
- 점수에 따른 등급 판별 (if문과 switch문)
- 90점 이상: A
- 80점 이상: B
- 70점 이상: C
- 60점 이상: D
- 그 외: F
- 윤년 판별 프로그램
- 윤년의 조건:
- 연도가 4로 나누어지고 100으로 나누어떨어지지 않거나 400으로 나누어떨어질 때
- 윤년의 조건:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class LeapYearChecker {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("연도를 입력하세요: ");
int year = scanner.nextInt();
if ((year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || year % 400 == 0) {
System.out.println(year + "년은 윤년입니다.");
} else {
System.out.println(year + "년은 윤년이 아닙니다.");
}
scanner.close();
}
}
Integer.parselnt(문자숫자) --> 숫자
Integer.toString(숫자) --- > 문자 숫자
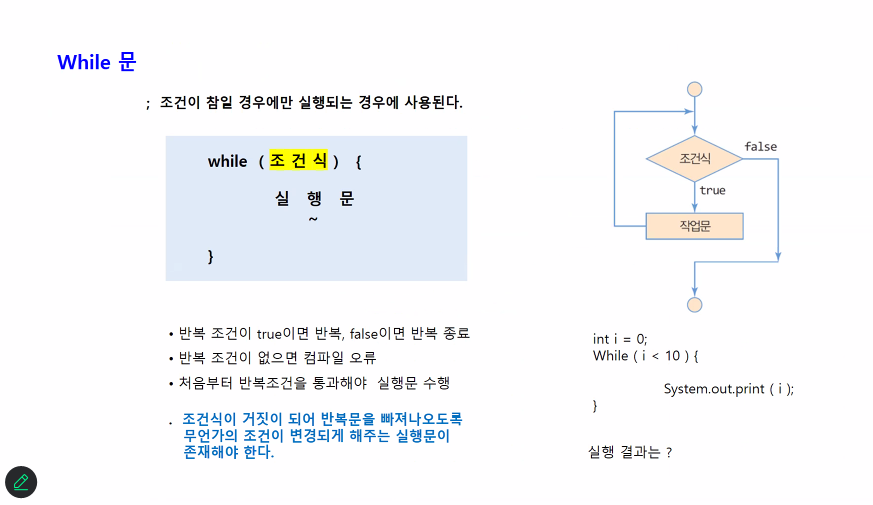
반복문
100까지 더하기
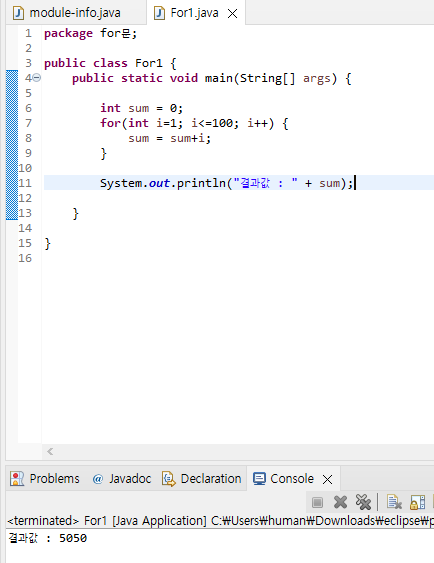
100까지 짝수만 더하기
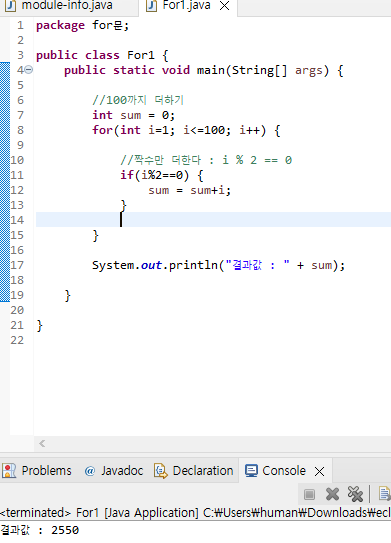
package for문;
public class For1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//100까지 더하기
int sum1 = 0;
int sum2 = 0;
for(int i=1; i<=100; i++) {
//짝수만 더한다 : i % 2 == 0
if(i%2==0) {
sum1 = sum1+i;
}
//홀수만 더한다 : i % 2 != 0
if(i%2!=0) {
sum2 = sum2+i;
}
}
System.out.println("짝수의 합 : " + sum1);
System.out.println("홀수의 합 : " + sum2);
}짝수의 합 : 2550
홀수의 합 : 2500
구구단 출력
package for문;
public class For2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// i,j,k를 사용한다.
// 구구단 출력 - 5단 *9수
/*
dan * su = 값
*/
for(int dan=1; dan<=5; dan++) { //단
for(int su=1; su<=9; su++) { //수
System.out.println(dan+"*"+su+"="+(dan*su));
}
}
}
}
1*1=1
1*2=2
1*3=3
1*4=4
1*5=5
1*6=6
1*7=7
1*8=8
1*9=9
2*1=2
2*2=4
2*3=6
2*4=8
2*5=10
2*6=12
2*7=14
2*8=16
2*9=18
3*1=3
3*2=6
3*3=9
3*4=12
3*5=15
3*6=18
3*7=21
3*8=24
3*9=27
4*1=4
4*2=8
4*3=12
4*4=16
4*5=20
4*6=24
4*7=28
4*8=32
4*9=36
5*1=5
5*2=10
5*3=15
5*4=20
5*5=25
5*6=30
5*7=35
5*8=40
5*9=45
package for문;
public class For3_ex {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. 1단~9단, 1수~9수 까지를 출력하시오
// 2. 짝수단만 출력하시오
// 3. 짝수단의 짝수수만 출력하시오.
for(int dan=1; dan<=9; dan++) { //단
for(int su=1; su<=9; su++) { //수
System.out.println(dan+"*"+su+"="+(dan*su));
}
System.out.println();
}
for(int dan=1; dan<=9; dan++) { //단
for(int su=1; su<=9; su++) { //수
if(dan % 2 == 0) {
System.out.println(dan+"*"+su+"="+(dan*su));
}
}
System.out.println();
}
for(int dan=1; dan<=9; dan++) { //단
for(int su=1; su<=9; su++) { //수
if(dan % 2 == 0 && su % 2 == 0) {
System.out.println(dan+"*"+su+"="+(dan*su));
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
1*1=1
1*2=2
1*3=3
1*4=4
1*5=5
1*6=6
1*7=7
1*8=8
1*9=9
2*1=2
2*2=4
2*3=6
2*4=8
2*5=10
2*6=12
2*7=14
2*8=16
2*9=18
3*1=3
3*2=6
3*3=9
3*4=12
3*5=15
3*6=18
3*7=21
3*8=24
3*9=27
4*1=4
4*2=8
4*3=12
4*4=16
4*5=20
4*6=24
4*7=28
4*8=32
4*9=36
5*1=5
5*2=10
5*3=15
5*4=20
5*5=25
5*6=30
5*7=35
5*8=40
5*9=45
6*1=6
6*2=12
6*3=18
6*4=24
6*5=30
6*6=36
6*7=42
6*8=48
6*9=54
7*1=7
7*2=14
7*3=21
7*4=28
7*5=35
7*6=42
7*7=49
7*8=56
7*9=63
8*1=8
8*2=16
8*3=24
8*4=32
8*5=40
8*6=48
8*7=56
8*8=64
8*9=72
9*1=9
9*2=18
9*3=27
9*4=36
9*5=45
9*6=54
9*7=63
9*8=72
9*9=81
2*1=2
2*2=4
2*3=6
2*4=8
2*5=10
2*6=12
2*7=14
2*8=16
2*9=18
4*1=4
4*2=8
4*3=12
4*4=16
4*5=20
4*6=24
4*7=28
4*8=32
4*9=36
6*1=6
6*2=12
6*3=18
6*4=24
6*5=30
6*6=36
6*7=42
6*8=48
6*9=54
8*1=8
8*2=16
8*3=24
8*4=32
8*5=40
8*6=48
8*7=56
8*8=64
8*9=72
2*2=4
2*4=8
2*6=12
2*8=16
4*2=8
4*4=16
4*6=24
4*8=32
6*2=12
6*4=24
6*6=36
6*8=48
8*2=16
8*4=32
8*6=48
8*8=64
package for문;
public class for4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int i=0; i <5; i++) {
for(int j=0; j<=i; j++) {
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println();
for(int i=5; i >=1; i--) {
for(int j=1; j<=i; j++) {
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println();
// *
// **
// ***
// ****
//*****
for(int i=5; i >=1; i--) {
for(int j=1; j<=5; j++) {
if(j>=i) {
System.out.print("*");
}
else
{
System.out.print(" ");
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
*
**
***
****
*****
*****
****
***
**
*
*
**
***
****
*****
package for문;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class For6_배수 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
. 몇까지의 수의 범위를 입력받는다
. 2의배수이면서 3의배수인 수만 더한다
1. Scanner
2. for
3. if
4. 2배수+3배수
*/
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("범위 N 입력");
int N = sc.nextInt();
int sum = 0;
sc.close();
for(int i = 1; i<=N; i++ ) {
if(i % 2 ==0 && i % 3 ==0)
{
sum += i;
}
}
System.out.println("2의배수이고 3의배수인값을 더한 결과는 " + sum);
}
}
범위 N 입력
24
2의배수이고 3의배수인값을 더한 결과는 60
package while문;
public class while3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int dan =1;
int su = 1;
while(dan<=9) {
while(su<=9) {
System.out.println(dan+"*"+su+"="+(dan*su));
su++;
}
dan++;
su = 1;
}
}
}1*1=1
1*2=2
1*3=3
1*4=4
1*5=5
1*6=6
1*7=7
1*8=8
1*9=9
2*1=2
2*2=4
2*3=6
2*4=8
2*5=10
2*6=12
2*7=14
2*8=16
2*9=18
3*1=3
3*2=6
3*3=9
3*4=12
3*5=15
3*6=18
3*7=21
3*8=24
3*9=27
4*1=4
4*2=8
4*3=12
4*4=16
4*5=20
4*6=24
4*7=28
4*8=32
4*9=36
5*1=5
5*2=10
5*3=15
5*4=20
5*5=25
5*6=30
5*7=35
5*8=40
5*9=45
6*1=6
6*2=12
6*3=18
6*4=24
6*5=30
6*6=36
6*7=42
6*8=48
6*9=54
7*1=7
7*2=14
7*3=21
7*4=28
7*5=35
7*6=42
7*7=49
7*8=56
7*9=63
8*1=8
8*2=16
8*3=24
8*4=32
8*5=40
8*6=48
8*7=56
8*8=64
8*9=72
9*1=9
9*2=18
9*3=27
9*4=36
9*5=45
9*6=54
9*7=63
9*8=72
9*9=81
package while문;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class while4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("숫자를 입력해 주세요");
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int num = 0;
double sum = 0;
int i = 0;
while((i=sc.nextInt()) != 0) { // 숫자이면 반복,0이면 중지
//sum = sum + i;
sum += i;
num++;
}
System.out.println("입력된 수의 개수는" + num+"개이며 평균은 "
+(sum/num)+"입니다.");
sc.close();
}
}숫자를 입력해 주세요
35
23
28
74
32
11
33
44
0
입력된 수의 개수는8개이며 평균은 35.0입니다.
package while문;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class while5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
1.임의의 수를 입력받는다
2. while문으로 1부터 입력받은 수까지 합산한다
3. 홀수 또는 3의 배수인 수만 합산한다
4. 결과를 출력한다
*/
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("숫자를 입력해 주세요 >>");
int num = sc.nextInt();
sc.close();
int i = 0;
double sum = 0;
double sum3 = 0;
while(i<=num)
{
sum += i;
if((i % 2 != 0) || (i % 3 == 0))
{
sum3 += i;
}
i++;
}
System.out.println("합산 :" + sum);
System.out.println("홀수 또는 3의 배수만 합산 :" + sum3);
}
}
숫자를 입력해 주세요 >>
33
합산 :561.0
홀수 또는 3의 배수만 합산 :379.0
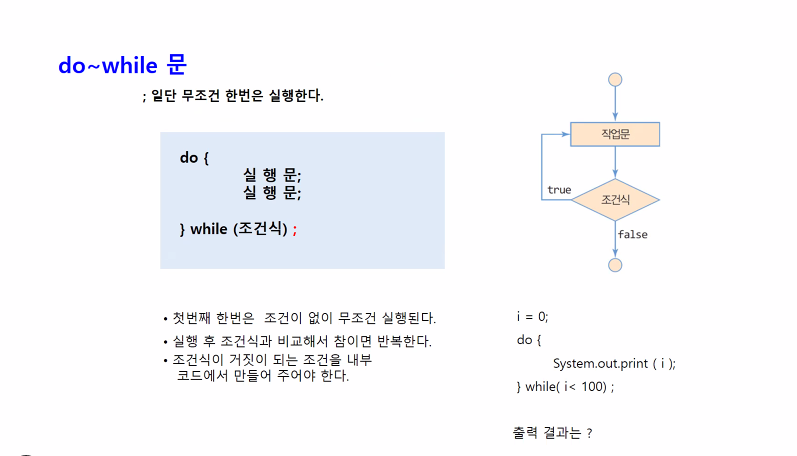
결과값: 30
package dowhile문;
public class dowhile1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//10까지 더하기
int sum = 0;
int i = 1;
do {
//짝수만 더하기
if(i%2 == 0) {
sum = sum + i;
}
i = i + 1; // i++ 동일
}while(i<=10);
System.out.println("결과값: " + sum);
}
}
package dowhile문;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class dowhile2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
1.임의의 수를 입력받는다
2. do while문을 이용해서 1~9단까지 출력한다
*/
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("임의의 수를 입력하세요 >>");
int num = sc.nextInt();
sc.close();
int i = 1; // 단을 나타내는 변수 (1단부터 시작)
do {
int j = 1; // 곱해지는 수 (1부터 시작)
System.out.println(i + "단:");
do {
System.out.println(i + " × " + j + " = " + (i * j));
j++;
} while (j <= 9); // j가 9 이하일 때까지 반복
System.out.println(); // 각 단 사이에 줄바꿈
i++;
} while (i <= num); // i가 N 이하일 때까지 반복
}
}
임의의 수를 입력하세요 >>
5
1단:
1 × 1 = 1
1 × 2 = 2
1 × 3 = 3
1 × 4 = 4
1 × 5 = 5
1 × 6 = 6
1 × 7 = 7
1 × 8 = 8
1 × 9 = 9
2단:
2 × 1 = 2
2 × 2 = 4
2 × 3 = 6
2 × 4 = 8
2 × 5 = 10
2 × 6 = 12
2 × 7 = 14
2 × 8 = 16
2 × 9 = 18
3단:
3 × 1 = 3
3 × 2 = 6
3 × 3 = 9
3 × 4 = 12
3 × 5 = 15
3 × 6 = 18
3 × 7 = 21
3 × 8 = 24
3 × 9 = 27
4단:
4 × 1 = 4
4 × 2 = 8
4 × 3 = 12
4 × 4 = 16
4 × 5 = 20
4 × 6 = 24
4 × 7 = 28
4 × 8 = 32
4 × 9 = 36
5단:
5 × 1 = 5
5 × 2 = 10
5 × 3 = 15
5 × 4 = 20
5 × 5 = 25
5 × 6 = 30
5 × 7 = 35
5 × 8 = 40
5 × 9 = 45
package breakcontinue문;
public class break1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
구구단(1~9단)에서 출력 과정에서 수가 1~5까지만 출력하시오
1*5=
2*5
3*5
*/
for(int i = 1; i<=9; i++) {
for(int j=1; j<=9; j++) {
if(j>=6) {
break; // break문을 만나면 아래코드를 실행하지않고 빠져나간다
}
System.out.println(i+"*"+j+"="+(i*j));
}
//여기로 빠져나온다
}
}
}
1*1=1
1*2=2
1*3=3
1*4=4
1*5=5
2*1=2
2*2=4
2*3=6
2*4=8
2*5=10
3*1=3
3*2=6
3*3=9
3*4=12
3*5=15
4*1=4
4*2=8
4*3=12
4*4=16
4*5=20
5*1=5
5*2=10
5*3=15
5*4=20
5*5=25
6*1=6
6*2=12
6*3=18
6*4=24
6*5=30
7*1=7
7*2=14
7*3=21
7*4=28
7*5=35
8*1=8
8*2=16
8*3=24
8*4=32
8*5=40
9*1=9
9*2=18
9*3=27
9*4=36
9*5=45
package breakcontinue문;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class break2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("몇까지 더할까요?");
int num = sc.nextInt();
int sum = 0;
int i = 1;
while(true) {
System.out.println(i);
if(i>num)
{
break;
}
sum+=i;
i++;
}
System.out.println("결과 : " + sum);
}
}몇까지 더할까요?
10
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
결과 : 55package breakcontinue문;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class break3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while(true) {
System.out.println("계속하시겠습니까(y/n)");
String answer = sc.next();
if(answer.equals("y")) {
break;
}
}
System.out.println("프로그램을 종료합니다.");
}
}
계속하시겠습니까(y/n)
n
계속하시겠습니까(y/n)
y
프로그램을 종료합니다.
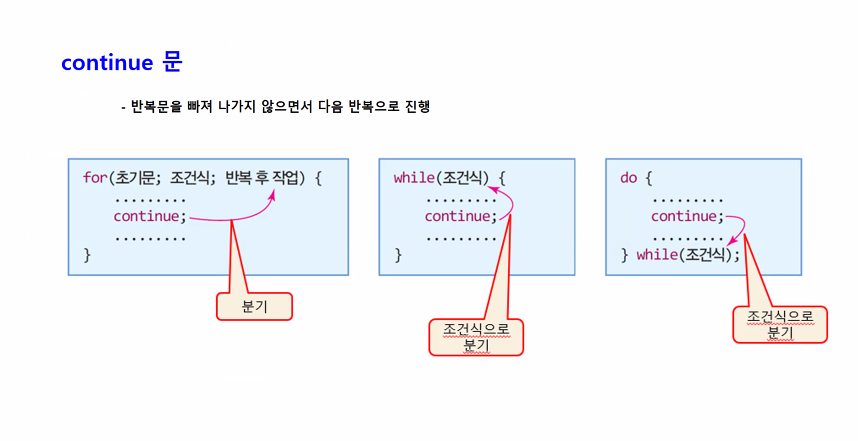
Cotinue문
package breakcontinue문;
public class continue1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//짝수 구하기
for(int i=1; i<=50; i++) {
if(i%2 == 0) {
System.out.print(i+" ");
}
}
System.out.println(); //줄바꿈용
//continue적용
for(int i=1; i<=50;i++) {
if(i%2==1) {
continue;
}
System.out.print(i+" ");
}
}
}2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 32 34 36 38 40 42 44 46 48 50
2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 32 34 36 38 40 42 44 46 48 50📚 통장 관리 프로그램 (break와 continue 사용)
🔹 문제 설명
- 통장 관리 프로그램을 작성합니다.
- 메뉴를 선택해 예금, 출금, 잔고조회, 종료 기능을 구현합니다.
- while문을 사용해 프로그램이 종료될 때까지 반복됩니다.
- break를 사용해 반복문을 종료합니다.
- 잘못된 메뉴를 선택하면 continue로 반복문의 처음으로 돌아갑니다.
🔹 코드 완성
package breakcontinue문;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class 통장관리 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int balance = 0; // 초기 잔고
while (true) {
// 메뉴 보여주기
System.out.println("===== 통장관리 프로그램 =====");
System.out.println("1. 예금");
System.out.println("2. 출금");
System.out.println("3. 잔고조회");
System.out.println("4. 종료");
System.out.print("메뉴를 선택하세요: ");
int menu = sc.nextInt(); // 메뉴 선택
if (menu == 1) {
// 예금 처리
System.out.print("예금할 금액을 입력하세요: ");
int deposit = sc.nextInt();
if (deposit > 0) {
balance += deposit;
System.out.println(deposit + "원이 예금되었습니다.");
} else {
System.out.println("올바른 금액을 입력하세요.");
}
} else if (menu == 2) {
// 출금 처리
System.out.print("출금할 금액을 입력하세요: ");
int withdraw = sc.nextInt();
if (withdraw > 0 && withdraw <= balance) {
balance -= withdraw;
System.out.println(withdraw + "원이 출금되었습니다.");
} else if (withdraw > balance) {
System.out.println("잔고가 부족합니다.");
} else {
System.out.println("올바른 금액을 입력하세요.");
}
} else if (menu == 3) {
// 잔고조회
System.out.println("현재 잔고: " + balance + "원");
} else if (menu == 4) {
// 종료
System.out.println("프로그램을 종료합니다.");
break;
} else {
// 잘못된 메뉴 선택
System.out.println("올바른 메뉴를 선택하세요 (1~4).");
continue; // 다음 반복으로 넘어감
}
System.out.println(); // 한 줄 띄우기
}
sc.close(); // Scanner 닫기
}
}===== 통장관리 프로그램 =====
1. 예금
2. 출금
3. 잔고조회
4. 종료
메뉴를 선택하세요: 1
예금할 금액을 입력하세요: 5000
5000원이 예금되었습니다.
===== 통장관리 프로그램 =====
메뉴를 선택하세요: 3
현재 잔고: 5000원
===== 통장관리 프로그램 =====
메뉴를 선택하세요: 2
출금할 금액을 입력하세요: 2000
2000원이 출금되었습니다.
===== 통장관리 프로그램 =====
메뉴를 선택하세요: 3
현재 잔고: 3000원
===== 통장관리 프로그램 =====
메뉴를 선택하세요: 4
프로그램을 종료합니다.
배열

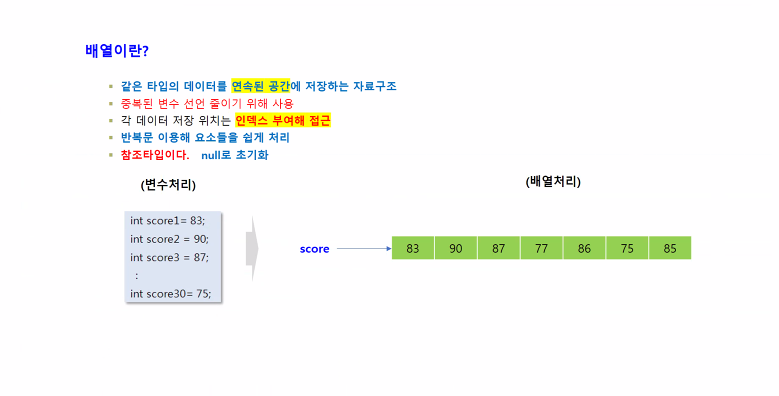
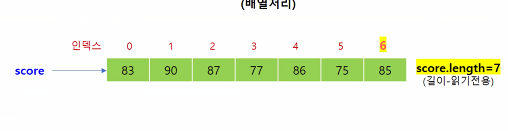

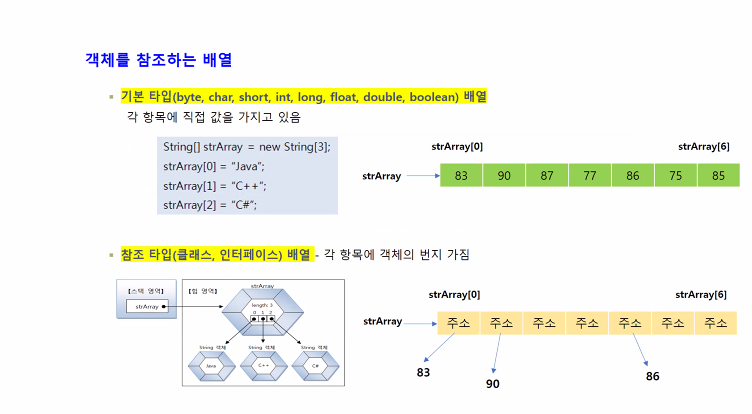

package array;
/*
배열
- 동일한 타임의 데이터를 연이어 저장할 수 있도록 하는 저장공간의 집합체
1. 선언
데이터타입 [] 배열명
2. 생성
배열명 = new 데이터타입[개수]
* 동시 선언/생성
데이터타입 [] 배열명 = new 데이터타입[개수];
3. 초기화
배열명[인덱스] = 값;
4. 활용
String str = 배열명[인덱스];
5. 읽고/수정/삭제... - CRUD
(그림) 0 1 2 3
배열명 -----------> [3][5][7][9][][][][][][] // 배열명.length
^ |
| v
배열명[인덱스] = 값 int num = 배열명[인덱스]
*/
public class Array1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//방법1
int[] intArr = new int[3]; //선언 intArr ------> [][][]
intArr[0] = 7;
intArr[1] = 8;
intArr[2] = 34;
//intArr[3] = 6; n >= intArr.length-1, n > intArr.length
//방법2
double[] doubleArr = new double[] {1,2,3,4,5,6};
//방법3
char[] charArr = {'가','나','다','라'};
// 읽기
String[] names = {"홍길동","이순신","강감찬"};
for(int i=0; i<names.length; i++) {
System.out.println("names["+i+"]="+ names[i]);
//특정한 것 찾기
if(names[i].equals("홍길동")) {
System.out.println("뛰어다닙니다");
//값수정
names[i] = "김길동";
}
}
// 확장for
for(String str : names) {
System.out.println(str);
if(str.equals("홍길동")) {
System.out.println("날라다닙니다");
}
}
}
}names[0]=홍길동
뛰어다닙니다
names[1]=이순신
names[2]=강감찬
김길동
이순신
강감찬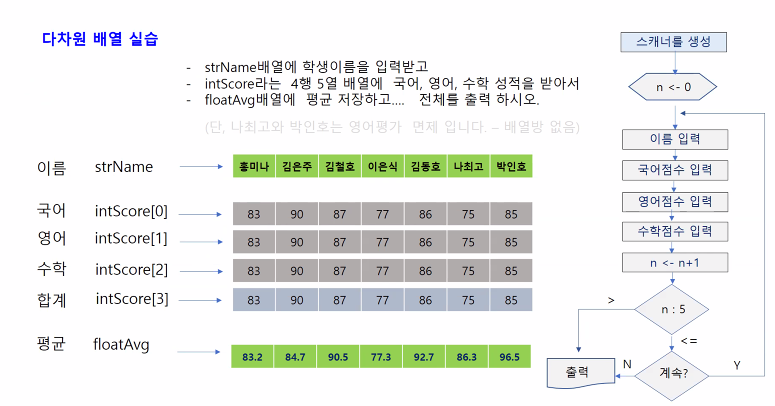
📚 학생 성적 관리 프로그램 (배열과 메뉴 구현)
🔹 문제 설명
- 10명의 학생 정보를 저장할 배열 생성
- 이름, 국어 점수, 영어 점수, 수학 점수, 총점
- 메뉴 기능 구현:
- 1. 등록: 학생 정보를 입력받아 저장
- 2. 전체검색: 모든 학생의 정보를 출력
- 3. 특정학생검색: 특정 학생의 정보를 검색 및 출력
- 4. 특정학생 kor 수정: 특정 학생의 국어 점수 수정
- 5. 종료: 프로그램 종료
🔹 완성된 코드
package array;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class array2_ex {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
// 배열 선언
String[] names = new String[10];
int[] kor = new int[10];
int[] eng = new int[10];
int[] math = new int[10];
int[] total = new int[10];
int studentCount = 0; // 등록된 학생 수
while (true) {
// 메뉴 출력
System.out.println("===== 학생 성적 관리 프로그램 =====");
System.out.println("1. 등록 | 2. 전체검색 | 3. 특정학생검색 | 4. 특정학생 kor 수정 | 5. 종료");
System.out.print("메뉴를 선택하세요: ");
int menu = scanner.nextInt();
switch (menu) {
case 1:
// 1. 등록
if (studentCount >= 10) {
System.out.println("더 이상 학생을 등록할 수 없습니다!");
break;
}
scanner.nextLine(); // 버퍼 비우기
System.out.print("학생 이름을 입력하세요: ");
names[studentCount] = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.print("국어 점수를 입력하세요: ");
kor[studentCount] = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.print("영어 점수를 입력하세요: ");
eng[studentCount] = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.print("수학 점수를 입력하세요: ");
math[studentCount] = scanner.nextInt();
total[studentCount] = kor[studentCount] + eng[studentCount] + math[studentCount];
System.out.println(names[studentCount] + " 학생이 등록되었습니다.\n");
studentCount++;
break;
case 2:
// 2. 전체검색
System.out.println("===== 전체 학생 목록 =====");
System.out.println("이름\t국어\t영어\t수학\t총점");
System.out.println("-----------------------------------");
for (int i = 0; i < studentCount; i++) {
System.out.printf("%s\t%d\t%d\t%d\t%d\n", names[i], kor[i], eng[i], math[i], total[i]);
}
System.out.println();
break;
case 3:
// 3. 특정학생검색
scanner.nextLine(); // 버퍼 비우기
System.out.print("검색할 학생 이름을 입력하세요: ");
String searchName = scanner.nextLine();
boolean found = false;
for (int i = 0; i < studentCount; i++) {
if (names[i].equals(searchName)) {
System.out.println("===== 학생 정보 =====");
System.out.printf("이름: %s | 국어: %d | 영어: %d | 수학: %d | 총점: %d\n",
names[i], kor[i], eng[i], math[i], total[i]);
found = true;
break;
}
}
if (!found) {
System.out.println("해당 이름의 학생을 찾을 수 없습니다.\n");
}
break;
case 4:
// 4. 특정학생 kor 수정
scanner.nextLine(); // 버퍼 비우기
System.out.print("국어 점수를 수정할 학생 이름을 입력하세요: ");
String updateName = scanner.nextLine();
boolean updated = false;
for (int i = 0; i < studentCount; i++) {
if (names[i].equals(updateName)) {
System.out.print("새로운 국어 점수를 입력하세요: ");
kor[i] = scanner.nextInt();
total[i] = kor[i] + eng[i] + math[i]; // 총점 업데이트
System.out.println(updateName + " 학생의 국어 점수가 수정되었습니다.\n");
updated = true;
break;
}
}
if (!updated) {
System.out.println("해당 이름의 학생을 찾을 수 없습니다.\n");
}
break;
case 5:
// 5. 종료
System.out.println("프로그램을 종료합니다.");
scanner.close();
return;
default:
System.out.println("올바른 메뉴를 선택하세요 (1~5).\n");
break;
}
}
}
}🔹 코드 설명
- 배열 선언
- names[]: 학생 이름
- kor[]: 국어 점수
- eng[]: 영어 점수
- math[]: 수학 점수
- total[]: 총점
- studentCount: 현재 등록된 학생 수
- 메뉴 선택 (switch-case)
- 1. 등록: 배열에 학생 정보를 저장하고 총점을 계산합니다.
- 2. 전체검색: 등록된 모든 학생의 정보를 출력합니다.
- 3. 특정학생검색: 입력받은 이름으로 학생을 검색하여 출력합니다.
- 4. 특정학생 kor 수정: 특정 학생의 국어 점수를 수정하고 총점을 재계산합니다.
- 5. 종료: 프로그램을 종료합니다.
- 입력 검증
- 학생이 10명을 초과하면 등록 불가 메시지 출력.
- 검색이나 수정 시 이름이 없을 경우 안내 메시지 출력.
🔹 입력 및 출력 예시
메뉴 선택 → 1 (등록)
학생 이름을 입력하세요: 홍길동
국어 점수를 입력하세요: 90
영어 점수를 입력하세요: 85
수학 점수를 입력하세요: 88
홍길동 학생이 등록되었습니다.
메뉴 선택 → 2 (전체검색)
이름 국어 영어 수학 총점
홍길동 90 85 88 263
메뉴 선택 → 3 (특정학생검색)
검색할 학생 이름을 입력하세요: 홍길동
이름: 홍길동 | 국어: 90 | 영어: 85 | 수학: 88 | 총점: 263
메뉴 선택 → 4 (특정학생 kor 수정)
국어 점수를 수정할 학생 이름을 입력하세요: 홍길동
새로운 국어 점수를 입력하세요: 95
홍길동 학생의 국어 점수가 수정되었습니다.
메뉴 선택 → 5 (종료)
프로그램을 종료합니다.🔹 포인트 정리
- 배열로 학생 정보 관리.
- switch-case로 메뉴 구현.
- 이름으로 특정 학생 검색 및 수정.
- 총점 실시간 업데이트.
LIST
'휴먼 IT 교육 수업 메모' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [휴먼IT] 휴먼IT 자바 수업 6일차 메모 (상속) 250109 (1) | 2025.01.09 |
|---|---|
| [휴먼IT] 휴먼IT JAVA 5일차 수업 메모 (상속) -250108 (0) | 2025.01.08 |
| [휴먼IT] 휴먼IT 자바 수업 4일차 메모 (예외처리,클래스와 객체) - 250107 (1) | 2025.01.07 |
| [휴먼IT] JAVA 수업 2일차 메모 (250103) (0) | 2025.01.03 |
| [휴먼IT] 자바 수업 1일차 메모 (250102) (0) | 2025.01.02 |


